A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF BODY COMPOSITION AND RELATIVE HEALTH STATUS AMONG RESIDENT AND NON-RESIDENT STUDENTS IN DIFFERENT SCHOOLS OF J&K
Keywords:
Residential, Non-Residential, Body Comnposition and Nutritional Status.Abstract
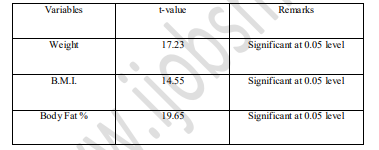
The purposes of the study were to find out body composition and relative health status of the resident and nonresident students in different schools of J&K and their comparison with each other. A total of 100 resident students in different schools of J&K and 10 non-resident students in different schools of J&K in between the age of 15 to 19 years were selected randomly from different resident and non-resident schools in the jammu region of J&K and comparison was done between these two groups. Height, Body weight, body fat percentage and body mass index were considered as variables for measurement of health and nutritional status in the investigation. All the variables were measured with the standard tools and equations. Mean and Standard deviation were calculated as descriptive statistics and to find out the inter group difference t-test was conducted. Result shows those resident students groups were superior in weight, PBF and BMI than non-resident students. Result also revealed that resident students group was in over weight zone in respect of BMI but non- resident students group was in the normal zone in this category. All the mean difference between these two groups was found statistically significant in this study
Metrics
References
Bandyopadhyay, N. (2007), “Studies on elderly women on their sedentary life style and on being active” Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kalyani, West Bengal.
Blair, S.N. et al. (1981). Interactions among dietary patter, physical activity and skin fold thickness, Research quarterly, 52 (4):777-782.
Chaine et al. (1989). Body mass index is a discriminate function among health-related variables and risk factors. J. Sports Med phys Fitness; 29(3):253-61
Joshi, A.R. Singh, R. and Joshi, A.R. (2008), Correlation of pulmonary function tests with body fat percentage in young individuals, Indian J. Phsiol Pharmacol, (52 (4), 383- 388.
Koley, S. Kaur,N and Sandhu, J.S. (2009). A Study on hand grip strength in female labourer of Jalandhar, Punjab, India, J Life Sci, 1 (1): 57-62.
McArdle, W.D. Katch, F.I. and Katch, V.L. (1996), Exercise physiology: Exercise, Nutrition and Human performance, Lea and Febiger: Balthinore (4th Ed).
Misra, K.B. Endemann, S.W. and Ayer, M. (2005), Leisure time physical activity and metabolic syndrome in Asian Indian Immigrants residing in Northern California. Ethnicity and Disease, Vol.15:625-634.
Saha Roy, G. (2010), Effect of Aerobic Training Programme on Active and Moderate Active NIDDM Female, Ph.D Thesis, Depart of Physical Education, University of Kalyani, West Bengal, India.
Tahara, Y. Moji, K. Aoyagi, K. Tsunawake, N. Murake, S. and Mascie-Taylor, C.G. (2016), Age related pattern of body density and body composition of Japanese men and women 18-59 years of age. National Institution of health, Am J Hum Biol, Vol. 14(6):743-52.
Upadhyay, S. Kumar, A.R. Singh, R. R. and Singh, B.B. (2011), Nutritional Status and Knowledge of Hill Women on Anemia: Effect of Various Socio-demographic Factors, J Hum Ecol, 33 (1): 29-34.
WHO (World Health Organization), 2016; http://apps.who.int/bmi/index
Wimberley, M.G. Milinda, M.M. Cathlin, W. Pamela, D.S. and Steven, S.C. (2016), Effects of habitual physical activity on the resting metabolic rates and body composition of women aged 35 to 50 years. J Am Diet Assoc. 100:1181-1188.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
© 2025 International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences. All Rights Reserved.
All content published in this journal, including articles, images, and other intellectual property, is protected by copyright law. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of the publisher.
For permissions and inquiries, please contact us at: editor@theuniversityacademics.com
License Terms for Publications in International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences
By submitting an article to the International Journal of Behavioral Social and Movement Sciences, authors agree to the following terms:
-
License Grant:
-
Authors retain copyright for their work. However, by submitting their work, authors grant the journal a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free license to publish, reproduce, distribute, display, and otherwise use the article in any form and medium (print or digital) in perpetuity.
-
-
Open Access:
-
Articles published in this journal are made freely available to the public under the terms of an open-access license. The journal allows anyone to access, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full text of the articles.
-
-
Attribution:
-
Authors are required to provide proper citation and attribution to the original article when reusing or referencing content. The attribution should include the author(s), title of the article, journal name, volume, issue, and publication year.
-
-
Reuse of Material:
-
Authors may reuse their published work for non-commercial purposes, including reprinting in other publications or personal websites, provided proper attribution is given to the original publication.
-
-
Creative Commons License:
-
The journal may publish articles under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which allows others to remix, adapt, and build upon the work, even for commercial purposes, as long as they give appropriate credit to the original author(s).
-
-
Peer Review:
-
The submitted article will undergo a thorough peer-review process, and the final decision regarding publication rests with the editorial board of the journal.
-
-
Withdrawal:
-
Once accepted for publication, articles may only be withdrawn with the approval of the editorial board and must not be published elsewhere in any form without prior written consent.
-












